Cant Miss Takeaways Of Info About Is 8 Layer PCB Good

China 8 Layer PCB Manufacturers, Suppliers And Factory
Decoding the 8-Layer PCB
1. Unveiling the Multi-Layered Mystery
Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) are the unsung heroes of modern electronics, the foundation upon which everything from your smartphone to your washing machine operates. When it comes to PCB complexity, the number of layers is a key factor. So, "Is 8 layer PCB good?" That's the million-dollar question, isn't it? Well, not literally a million dollars, hopefully! But it's a valid and important query.
Think of a PCB like a multi-story building. A single-layer PCB is like a one-story shack, simple but limited. An 8-layer PCB, on the other hand, is a more sophisticated structure, offering significantly more space and flexibility for routing circuits and managing signal integrity. Deciding whether it's 'good' depends entirely on your project's needs.
At its core, an 8-layer PCB has eight conductive layers of copper, separated by insulating materials. This increased layering allows for greater circuit density and improved electromagnetic compatibility (EMC). It's like having eight different highways for your electronic signals to travel on, minimizing traffic jams and interference.
However, all this complexity comes with a price. 8-layer PCBs are more expensive to manufacture and require more sophisticated design tools and expertise. So, before you jump on the 8-layer bandwagon, let's explore the pros and cons in more detail.
The Good Stuff
2. Advantages That Make a Difference
The primary reason to opt for an 8-layer PCB is increased circuit density. If you're designing a complex electronic device with many components, an 8-layer PCB provides the space you need to route all the necessary connections efficiently. Think of it as organizing your messy desk; more drawers mean more organization!
Improved signal integrity is another significant advantage. With more layers, you have greater control over impedance matching and signal routing, reducing the risk of signal reflections and distortions. This is crucial for high-speed digital circuits where signal quality is paramount. Nobody wants their data corrupted!
Enhanced EMC performance is also a key benefit. The extra layers provide more opportunities for ground planes and power planes, which help to shield sensitive circuits from electromagnetic interference (EMI) and reduce radiated emissions. This can be crucial for meeting regulatory requirements and ensuring the reliable operation of your device.
Furthermore, 8-layer PCBs can often lead to miniaturization. By routing more circuits in a smaller area, you can reduce the overall size of your electronic device. In a world where everything is getting smaller and more portable, this is a significant advantage.

CuttingEdge 8Layer PCB For Mobile Gadgets China Advanced
The Not-So-Good Stuff
3. Considerations Before You Commit
Of course, there are also some potential downsides to consider. The biggest one is cost. 8-layer PCBs are significantly more expensive to manufacture than simpler PCBs. This is due to the increased complexity of the manufacturing process and the higher material costs. Budget is always a factor, isn't it?
Increased design complexity is another concern. Designing an 8-layer PCB requires more expertise and more sophisticated design tools. You'll need to be proficient in PCB design software and have a good understanding of signal integrity and EMC principles. It's not as simple as drawing lines on a piece of paper.
Longer lead times can also be an issue. Because of the increased complexity, 8-layer PCBs typically take longer to manufacture than simpler PCBs. This can be a problem if you're on a tight schedule. Patience is a virtue, but sometimes time is money!
Finally, rework and repair can be more difficult. If something goes wrong with an 8-layer PCB, it can be more challenging to diagnose and fix than with a simpler PCB. This is because the internal layers are harder to access and the traces are more densely packed. Think of it like trying to untangle a really knotted ball of yarn.

Making the Decision
4. Factors to Weigh Carefully
So, how do you decide if an 8-layer PCB is the right choice for your project? Well, first, you need to assess the complexity of your design. If you're designing a simple circuit with few components, a single- or double-layer PCB may be sufficient. But if you're designing a complex electronic device with many components and high-speed signals, an 8-layer PCB may be necessary.
Next, consider your budget. 8-layer PCBs are more expensive, so you need to make sure you can afford the additional cost. Get quotes from different PCB manufacturers and compare prices. Don't forget to factor in the cost of design tools and expertise.
Also, think about your schedule. 8-layer PCBs take longer to manufacture, so you need to factor this into your project timeline. If you're on a tight schedule, you may need to consider a simpler PCB or find a manufacturer that can offer faster turnaround times.
Finally, consider the long-term implications. An 8-layer PCB may be more expensive upfront, but it could save you money in the long run by improving signal integrity, reducing EMI, and enabling miniaturization. It's like investing in a good pair of shoes; they may cost more initially, but they'll last longer and be more comfortable.

8 Layer PCB Everything You Need To Know PCBA Manufacturers
Alternatives to 8-Layer PCBs
5. Exploring Other Options
If an 8-layer PCB seems like overkill or is too expensive, consider these alternatives. Perhaps, you can optimize your existing design to reduce complexity. Rework your schematic, choose different components, or explore clever layout techniques to minimize the number of layers required. Sometimes, a little ingenuity can go a long way!
Another option is to use a 4-layer or 6-layer PCB. These are less expensive than 8-layer PCBs but still offer some of the benefits of multi-layer designs. They're a good compromise if you need more routing space than a single- or double-layer PCB but don't need the full capabilities of an 8-layer PCB.
Flex PCBs or rigid-flex PCBs are also viable alternatives for certain applications. These PCBs can be bent or folded to fit into tight spaces, reducing the overall size of your device. They're often used in applications where space is at a premium, such as wearable devices and medical implants.
Finally, you can consider using a combination of different PCB technologies. For example, you could use a single-layer PCB for simple analog circuits and a multi-layer PCB for complex digital circuits. This can help you optimize cost and performance for different parts of your design.

FAQ
6. Your Burning Questions Answered
Here are some common questions about 8-layer PCBs:
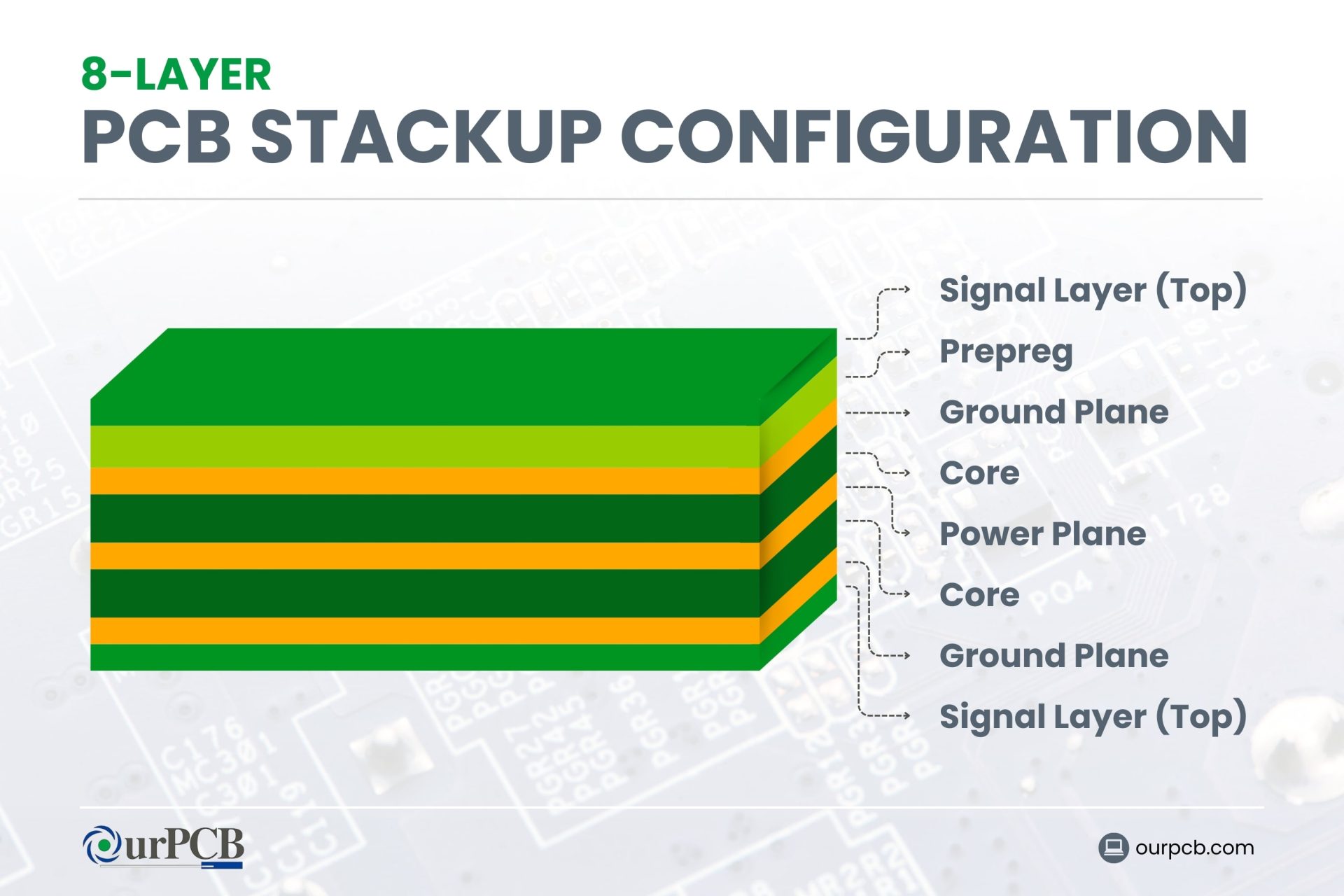
7. What is the typical layer stackup for an 8-layer PCB?
A typical 8-layer stackup might include signal layers on the top and bottom, ground and power planes in the middle, and additional signal layers between. The exact arrangement depends on the specific design requirements and signal routing needs.
8. Are 8-layer PCBs more difficult to assemble?
Assembly complexity can increase due to the higher density of components and routing. However, modern assembly techniques and equipment can handle 8-layer PCBs effectively. Proper design for manufacturability (DFM) is crucial.
9. When is it absolutely necessary to use an 8-layer PCB?
It's often necessary for high-speed digital designs, complex analog circuits, or applications requiring tight EMC control. Essentially, if you're pushing the limits of performance or miniaturization, an 8-layer PCB might be the only way to go.